在 AI PC 上本地微调 LLM:不用独显,也能把 Llama 3.2 训练成“会调用工具”的模型
本文分享一个真实跑通的案例:在AI PC上,使用 Unsloth 进行 LoRA 微调,对 meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct 进行训练,让模型具备 Function Calling(工具调用) 能力,并完成推理与评测。
作者: 武卓,胡誉文
什么是 AI PC?为什么它适合做本地微调
AI PC(AI 个人电脑)正在把“推理 + 微调”从云端带回本地:它通常具备更强的端侧算力组合(CPU / iGPU / NPU 等),让开发者可以在不依赖昂贵独立显卡、甚至不必上云的情况下,通过 LoRA 等参数高效方法,完成SFT (Supervised Fine-Tuning)这类微调任务。
对开发者来说,AI PC 最大的价值在于“高频迭代”:
-
快速验证你的数据、Prompt、工具调用格式是否有效
-
不用为了短平快实验频繁开云实例,成本更可控
-
数据不出本机,适合企业/内部 PoC 或敏感数据场景
本文分享一个真实跑通的案例:在AI PC 上,使用 Unsloth 进行 LoRA 微调(基于Transformer Reinforcement Learning(TRL) 的 SFTTrainer),对 meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct 进行训练,让模型具备 Function Calling(工具调用) 能力,并完成推理与评测。
-
训练数据集:hiyouga/glaive-function-calling-v2-sharegpt
-
评测数据集:Salesforce/xlam-function-calling-60k(需要申请权限)
从 0 到 1:按步骤搭环境并跑通微调
第 0 步:打开终端窗口
-
例如:打开 Anaconda Prompt
-
conda activate ...
第 1 步:安装 Visual Studio C++ 工具链
可在如下链接(https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/zh-hans/downloads/?q=build+tools)下载并安装 Visual Studio Build Tools / Community ,安装时勾选:
-
Desktop development with C++
-
MSVC v143 toolset
-
Windows 10/11 SDK
(可选)在当前终端启用 MSVC,运行以下命令可以验证(根据目前的安装版本和路径,以下路径名可能会有所不同:
call "C:\Program Files\Microsoft VisualStudio\18\Community\VC\Auxiliary\Build\vcvars64.bat"where cl
确认能看到 cl.exe 路径,说明编译器 OK。
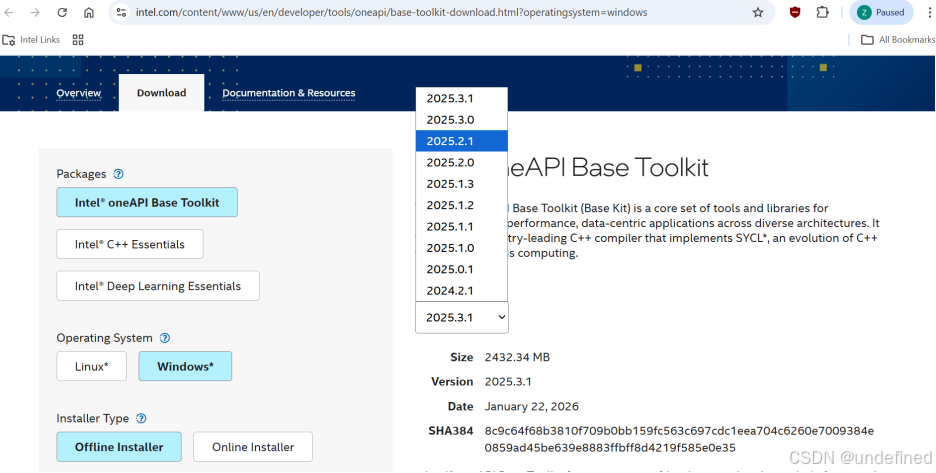
第 2 步:安装 Intel oneAPI(Intel GPU/XPU 路线)
安装 oneAPI Base Toolkit 2025.2.1版本,点击https://www.intel.cn/content/www/cn/zh/developer/tools/oneapi/base-toolkit-download.html 的安装包下载安装。
需初始化 oneAPI 环境变量:
call "C:\Program Files (x86)\Intel\oneAPI\setvars.bat" 第 3 步:开启 Windows 长路径(只需一次)
管理员 CMD终端窗口执行:
powershell -Command "Set-ItemProperty -Path""HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\FileSystem"" -Name ""LongPathsEnabled"" -Value 1
第 4 步:创建 Conda 环境并安装 Unsloth(Intel XPU 版本)
conda create -n aipc-finetune-example python=3.11 -yconda activate aipc-finetune-examplegit clone https://github.com/unslothai/unsloth.gitcd unslothpip install -e .[intel-gpu-torch290]
安装完成后,你可以快速确认 XPU 可用:
import torchprint(torch.__version__) # 2.9.0+xpuprint(hasattr(torch, "xpu") and torch.xpu.is_available()) # True
第 5 步:配置 Level Zero SDK
Triton Intel 后端 JIT 编译依赖 Level Zero headers,在这里https://github.com/oneapi-src/level-zero/releases/tag/v1.20.2 下载 level-zero-win-sdk-1.20.2.zip 并解压到例如:
C:\Users\MindPro\On-Device Fine-tuning AIPC Example\level-zero-win-sdk-1.20.2设置 ZE_PATH:
set ZE_PATH=C:\Users\MindPro\On-Device Fine-tuning AIPC Example\level-zero-win-sdk-1.20.2第 6 步:Hugging Face gated 数据集访问(评测必看)
评测数据集 Salesforce/xlam-function-calling-60k 是 gated:仅设置 HF_TOKEN 不够,还需要在网页上 Request access / Agree。
推荐流程:
set HF_TOKEN=hf_xxxhuggingface-cli login
然后去数据集页面申请/同意一次。
第 7步:安装 ROUGE 评测依赖
pip install -U evaluate nltk rouge_score bert_score absl-pypython -c"import nltk; nltk.download('punkt')"
3)运行:训练 / 推理 / 评测
-
训练
call "C:\Program Files (x86)\Intel\oneAPI\setvars.bat" --forceset ZE_PATH=path\to\the\unzipped\level-zero-win-sdk-1.20.2 #这里放你自己的解压后的路径set UNSLOTH_DISABLE_STATISTICS=1python train.py
具体代码如下:
import datetimefrom datasets import load_datasetimport torchfrom unsloth import FastLanguageModelfrom trl import SFTTrainer, SFTConfigfrom unsloth.chat_templates import get_chat_templatedef prepare_dataset(tokenizer, dataset_name, dataset_size, dataset_seed):system_prompt = "You are a helpful assistant with access to the following functions. Use them if required -\n__TOOL_DESCRIPTION__\nTo use these functions respond with:\n{\"name\": \"function_name\", \"arguments\": {\"arg_1\": \"value_1\", \"arg_1\": \"value_1\", ...}}\n\nEdge cases you must handle:\n - If there are no functions that match the user request, you will respond politely that you cannot help."def formatting_prompts_func(example):texts = []""" for query, tools, answers in zip(example['query'], example['tools'], example['answers']):system_prompt = system_prompt.replace("__TOOL_DESCRIPTION__", tools)messages = [{"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},{"role": "user", "content": query},{"role": "assistant", "content": answers},] """for messages, tools in zip(example["conversations"], example["tools"]):messages.insert(0, {"from": "system", "value": system_prompt.replace("__TOOL_DESCRIPTION__", tools)})text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,tokenize=False,add_generation_prompt=False)texts.append(text)return {"text": texts}dataset = load_dataset(dataset_name, split="train").select(range(dataset_size)).shuffle(seed=dataset_seed)print(dataset)dataset = dataset.map(formatting_prompts_func, batched=True)for i in range(3):print(f"Sample {i}:\n{dataset[i]['text']}\n{'='*40}")return datasetdef get_tokenizer(tokenizer):tokenizer = get_chat_template(tokenizer,mapping={"role": "from","content": "value","user": "human","assistant": "gpt",},chat_template="llama-3.1",)return tokenizerdef main(repo_id_or_model_path="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct",epochs=1,max_seq_length=2048,dataset_size=2000,lora_rank=16,batch_size=2,learning_rate="2e-4",max_steps=None,logging_steps=50,gradient_accumulation_steps=1,random_state=3407,dataset_seed=None,output_dir=None,):dataset_name = "hiyouga/glaive-function-calling-v2-sharegpt"optim = "adamw_torch"use_gradient_checkpointing = "unsloth"dtype = torch.bfloat16def start_train(trainer):return trainer.train()lora_kwargs = {"r": lora_rank, # Choose any number > 0 ! Suggested 8, 16, 32, 64, 128"target_modules": ["q_proj", "k_proj", "v_proj", "o_proj", "gate_proj", "up_proj", "down_proj"],"lora_alpha": 16,"lora_dropout": 0, # Supports any, but = 0 is optimized"bias": "none", # Supports any, but = "none" is optimized"use_rslora": False,"loftq_config": None,}training_args_kwargs = {}checkpoint_output_dir = f"{outputs}/checkpoints"if max_steps is not None:training_args_kwargs["max_steps"] = max_stepsmodel, tokenizer_orig = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(model_name=repo_id_or_model_path,max_seq_length=max_seq_length,dtype=dtype,full_finetuning=False,load_in_4bit=False,device_map="xpu:0",use_gradient_checkpointing=use_gradient_checkpointing,)model = FastLanguageModel.get_peft_model(model,random_state=random_state,**lora_kwargs)print(">>> Success to load model!")tokenizer = get_tokenizer(tokenizer_orig)dataset = prepare_dataset(tokenizer, dataset_name, dataset_size, dataset_seed)print(">>> Success to create datasets!")training_arguments = SFTConfig(per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,gradient_accumulation_steps=gradient_accumulation_steps,warmup_steps=5,num_train_epochs=epochs,learning_rate=float(learning_rate),fp16=True if dtype == torch.float16 else False,bf16=True if dtype == torch.bfloat16 else False,logging_steps=logging_steps,optim=optim,weight_decay=0.01,lr_scheduler_type="linear",seed=random_state,output_dir=checkpoint_output_dir,report_to="none",dataset_text_field="text",dataset_num_proc=1,packing=False,**training_args_kwargs,)trainer = SFTTrainer(model = model,tokenizer = tokenizer_orig,train_dataset = dataset,args = training_arguments)print(">>> Success to define trainer!")print(f"Starting training with:\nrandom_state: {random_state}\nepochs: {epochs}\nbatch_size: {batch_size}\ndataset_size: {dataset_size}\nlora_rank: {lora_rank}\nlearning_rate: {learning_rate}\nmax_steps: {max_steps}\nlogging_steps: {logging_steps}\ngradient_accumulation_steps: {gradient_accumulation_steps}")trainer_stats = start_train(trainer)print(trainer_stats)print("Total Time: ", str(datetime.timedelta(seconds=int(trainer_stats.metrics["train_runtime"]))))if __name__ == "__main__":# Set params accordinglymain()
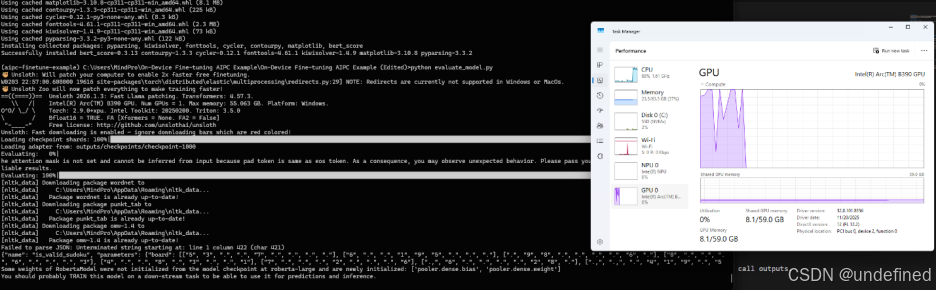
运行效果如下:
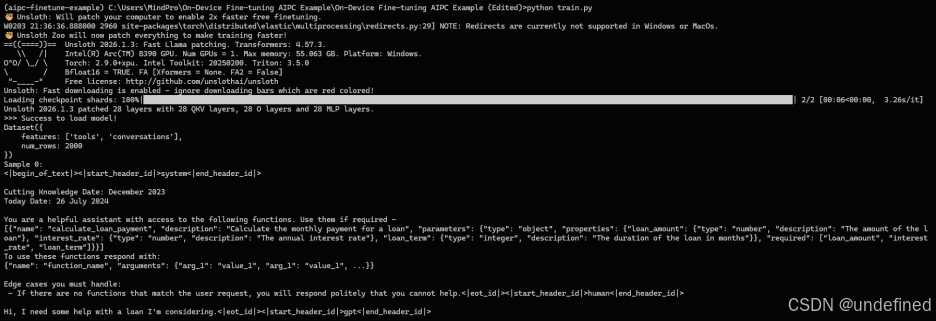
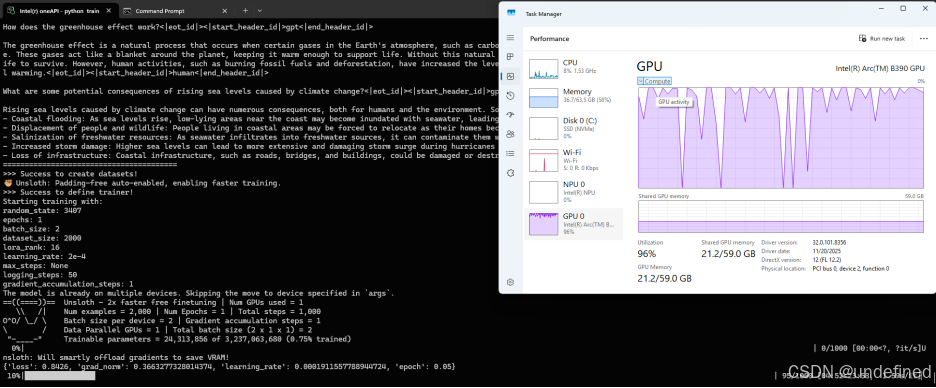
(以上截图不代表性能数据,实际性能
会由于硬件类型和系统环境等浮动)
-
推理
具体代码如下:
import osimport jsonimport stringimport randomfrom unsloth import FastLanguageModelfrom sample_tools import (weather_info,send_email,search_web,create_calendar_event,create_calendar_event_with_attendees,translate_text,set_reminder,generate_password,update_calendar,get_vector_sum,)def generate_alphanumeric():characters = string.ascii_letters + string.digitsresult = ''.join(random.choice(characters) for _ in range(9))return resultdef parse_tool_call(decoded_output):try:content = json.loads(decoded_output[0])except json.JSONDecodeError as e:print("Failed to parse JSON:", e)print("----end----\n\n")return None, Nonetry:function_name = content['name']arguments = content['parameters']except KeyError as e:print("Missing key in JSON:", e)print("----end----\n\n")return None, Nonereturn function_name, argumentsdef call_tool(function_name, arguments):try:result = globals()[function_name](**arguments)print("Tool call result: ", result)return resultexcept Exception as e:print("Error calling function:", e)return Nonedef inference(model, tokenizer, query, tools, generation_args):"""Inference function to process user queries.The model generates a JSON tool call based on the user query, which is then parsed and executed."""print("----start----")messages = [# {"role": "system", "content": system_prompt},{"role": "user", "content": query},]input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,tokenize=True,add_generation_prompt=True,add_special_tokens=False,padding=True,tools=tools,return_tensors="pt",).to("xpu")output = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids,do_sample=False,# repetition_penalty=1.1,num_return_sequences=1,**generation_args)generated_tokens = output[:, input_ids.shape[1]:]decoded_output = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)print("Assistant response:", decoded_output[0])function_name, arguments = parse_tool_call(decoded_output)if not function_name or not arguments:returnresult = call_tool(function_name, arguments)tool_calls = [{"id": generate_alphanumeric(),"type": "function","function": {"name": function_name,"arguments": arguments}}]messages.append({"role": "assistant","tool_calls": tool_calls})messages.append({"role": "tool","name": function_name,"content": result})messages.append({"role": "assistant","content": "Given the tool response, give the final answer to the user. Answer:\n"})tool_prompt = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,system_prompt=None,continue_final_message=True,add_special_tokens=True,return_tensors="pt",return_dict=True,tools=None,).to("xpu")tool_prompt = tool_prompt.to(model.device)out = model.generate(**tool_prompt,**generation_args)generated_text = out[0, tool_prompt['input_ids'].shape[1]:]print("Assistant response:", tokenizer.decode(generated_text, skip_special_tokens=True))print("----end----\n\n")def main(repo_id_or_model_path="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct",disable_adapter=False,lora_adapter_path="outputs/checkpoints/checkpoint-1000",max_seq_length=2048,max_new_tokens=150,temperature=None,top_p=None,top_k=None,min_p=None,):model = "meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct"model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(model_name=repo_id_or_model_path,max_seq_length=max_seq_length,dtype=None,load_in_4bit=False,fix_tokenizer=False)if not disable_adapter:if os.path.exists(lora_adapter_path):print("Loading adapter from:", lora_adapter_path)model.load_adapter(lora_adapter_path)else:print(f"Adapter path {lora_adapter_path} does not exist.")raise FileNotFoundError(f"Adapter path {lora_adapter_path} does not exist.")generation_args = {k: v for k, v in {"max_new_tokens": max_new_tokens,"temperature": temperature,"top_p": top_p,"top_k": top_k,"min_p": min_p,}.items() if v is not None}queries = [("Find the sum of a = [1, -1, 2] and b = [3, 0, -4].", [update_calendar, get_vector_sum]),("Set a reminder to call John at 3 PM tomorrow.", [update_calendar, set_reminder, send_email]),("Generate a password for me. I want it to be 12 characters long, with numbers and symbols.", [generate_password, weather_info]),("Hey, I need to add an event to my calendar. It's a meeting with my team on 15th March from 10 AM to 12 PM. The title should be \"Team Meeting\".", [update_calendar, create_calendar_event, translate_text]),("Create a calendar event with the title 'Meeting' starting at 10 AM and ending at 12 PM on the 15th of March 2024, with attendees John and Jane.", [create_calendar_event, create_calendar_event_with_attendees]),]for query, tools in queries:inference(model, tokenizer, query, tools, generation_args)if __name__ == "__main__":# Set params accordinglymain()
其运行需要依赖的sample_tools.py的文件代码如下:
sample_tool.py具体代码如下:
def send_email(recipient: str, subject: str, body: str) -> dict:"""Send an email to a recipient.Args:recipient: Recipient email address.subject: Email subject.body: Email body.Returns:dict: Status and message about the sent email."""return {"status": "success", "message": f"Email sent to {recipient} with subject '{subject}'."}def weather_info(location: str) -> dict:"""Get weather information for a location.Args:location: Location to get weather info for.Returns:dict: Status and weather information for the location."""return {"status": "success", "weather": f"Weather info for {location}."}def search_web(query: str) -> dict:"""Search the web for information.Args:query: Search query.Returns:dict: Status and search results for the query."""return {"status": "success", "result": f"Search results for '{query}'."}def create_calendar_event(title: str, start_time: str, end_time: str) -> dict:"""Create a calendar event.Args:title: Event title.start_time: Start time.end_time: End time.Returns:dict: Status and message about the created event."""return {"status": "success", "message": f"Event '{title}' created from {start_time} to {end_time}."}def create_calendar_event_with_attendees(title: str, start_time: str, end_time: str, attendees: list[str] = None) -> dict:"""Create a calendar event with attendees.Args:title: Event title.start_time: Start time (ISO format).end_time: End time (ISO format).attendees: List of attendee email addresses.Returns:dict: Status and message about the created event with attendees."""attendees_list = attendees if attendees else []return {"status": "success","message": f"Event '{title}' created from {start_time} to {end_time} with attendees: {', '.join(attendees_list) if attendees_list else 'None'}."}def translate_text(text: str, target_language: str) -> dict:"""Translate text to another language.Args:text: Text to translate.target_language: Target language.Returns:dict: Status and translation result."""return {"status": "success", "translation": f"Translated '{text}' to {target_language}."}def set_reminder(reminder_text: str, time: str) -> dict:"""Set a reminder at a specific time.Args:reminder_text: Reminder text.time: Time for the reminder.Returns:dict: Status and message about the set reminder."""return {"status": "success", "message": f"Reminder set: '{reminder_text}' at {time}."}def generate_password(length: int, include_numbers: bool = False, include_symbols: bool = False) -> dict:"""Generate a random password.Args:length: The length of the password.include_numbers: Whether to include numbers in the password.include_symbols: Whether to include symbols in the password.Returns:dict: Status and the generated password."""import randomimport stringchars = string.ascii_lettersif include_numbers:chars += string.digitsif include_symbols:chars += string.punctuationpassword = ''.join(random.choice(chars) for _ in range(length))return {"status": "success", "password": password}def update_calendar(event_title: str, start_time: str, end_time: str) -> dict:"""Update a calendar with an event.Args:event_title: Event Title.start_time: Start Time.end_time: End Time.Returns:dict: Status and message about the updated calendar event."""return {"status": "success", "message": f"Event '{event_title}' has been successfully added to your calendar from {start_time} to {end_time}."}def get_vector_sum(a: list[float], b: list[float]) -> list[float]:"""Performs element-wise addition of two numerical vectors.Both vectors must be of the same length and contain numerical values.Args:a: First vector containing numerical valuesb: Second vector containing numerical valuesReturns:Resulting vector where each element is the sum of corresponding elements in a and bRaises:ValueError: If vectors have different lengthsExample:>>> get_vector_sum([1, 2], [3, 4])[4, 6]"""if len(a) != len(b):raise ValueError("Vectors must be of the same length")return [x + y for x, y in zip(a, b)]
运行效果如下:
python inference.py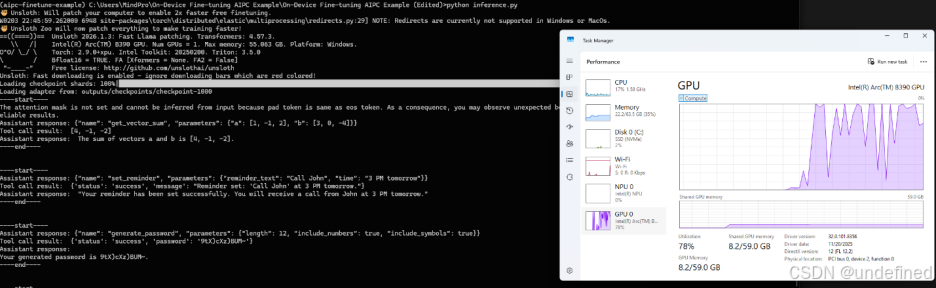
-
评测
python evaluate_model.py具体代码如下:
import osimport jsonfrom unsloth import FastLanguageModelfrom datasets import load_datasetfrom evaluate import load as load_metricfrom tqdm import tqdmdef get_dataset(dataset_name: str, num_samples: int, dataset_seed: int):dataset = load_dataset(dataset_name, split="train")dataset = dataset.shuffle(seed=dataset_seed)valid_examples = []for example in dataset:answer = json.loads(example["answers"])if len(answer) == 1:example["answers"] = example["answers"].replace('arguments', 'parameters')valid_examples.append(example)if len(valid_examples) == num_samples:breakreturn valid_examplesdef generate_response(model,tokenizer,query: str,tools: list[dict],generation_args: dict):messages = [{"role": "user", "content": query},]input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,tokenize=True,add_generation_prompt=True,add_special_tokens=False,padding=True,tools=tools,return_tensors="pt",).to("xpu")output = model.generate(input_ids=input_ids,do_sample=False,# repetition_penalty=1.1,num_return_sequences=1,**generation_args)generated_tokens = output[:, input_ids.shape[1]:]return tokenizer.decode(generated_tokens[0], skip_special_tokens=True)def parse_tool_call(prediction):"""Parses the model's prediction to extract the function name and parameters."""try:content = json.loads(prediction)except json.JSONDecodeError as e:print("Failed to parse JSON:", e)print(prediction)return None, Nonetry:function_name = content['name']arguments = content['parameters']except KeyError as e:print("Missing key in JSON:", e)return None, Nonereturn function_name, argumentsdef tool_call_metric(predictions: list[str], references: list[str]):"""Computes the accuracy of function calls based on function name and parameters.Instead of just exact matches this metric checks if the function name and parameters match."""correct = 0total = len(predictions)tool_call_results =[]for pred, ref in zip(predictions, references):pred_funcname, pred_args = parse_tool_call(pred)ref_funcname, ref_args = parse_tool_call(ref)if pred_funcname == ref_funcname and pred_args == ref_args:correct += 1match = Trueelse:match = Falsetool_call_results.append(match)accuracy = correct / total if total > 0 else 0.0return tool_call_results, {"tool_call_accuracy": accuracy}def evaluate_model(model,tokenizer,dataset: list[dict],generation_args: dict):"""Evaluates the model and returns predictions and references."""predictions = []references = []for example in tqdm(dataset, desc="Evaluating", unit="sample"):query = example["query"]reference = json.dumps(json.loads(example["answers"])[0]) # get first item as stringtools = json.loads(example["tools"])prediction = generate_response(model, tokenizer, query, tools, generation_args)predictions.append(prediction)references.append(reference)return predictions, referencesdef format_metric(metric):if isinstance(metric, dict):return {k: float(v) if hasattr(v, 'item') else v for k, v in metric.items()}elif hasattr(metric, 'item'):return float(metric)return metricdef log_evaluation_results(output_dir: str,evaluation_config: dict,predictions: list[str],references: list[str],dataset: list[dict],metrics: dict,tool_call_results: list[bool],output_filename="evaluation_results.json"):"""Logs evaluation metrics and predictions to a file."""print(tool_call_results)output_filepath = os.path.join(output_dir, output_filename)os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(output_filepath), exist_ok=True)results = {"evaluation_config": evaluation_config,"metrics": metrics,"predictions": [{"query": ex["query"],"tools": ex["tools"],"reference": reference,"prediction": pred,"match": tool_call_result} for ex, pred, reference, tool_call_result in zip(dataset, predictions, references, tool_call_results)]}with open(output_filepath, "w") as f:json.dump(results, f, indent=2)print(f"Outputs saved to {output_filepath}")def compute_metrics(output_dir, predictions: list, references: list, disable_save_results: bool, dataset: list):# Load metricsexact_match_metric = load_metric("exact_match")rouge_metric = load_metric("rouge")bleu_metric = load_metric("bleu")meteor_metric = load_metric("meteor")bertscore_metric = load_metric("bertscore")# Exact Match - Ignore whitespaces after semicolon. The model sometimes produces no-space after colon, which is still valid JSON.tool_call_results, tool_call_accuracy = tool_call_metric(predictions, references)exact_match_result = format_metric(exact_match_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references, regexes_to_ignore=[r"(?<=:)\s+"]))rouge_result = format_metric(rouge_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references))bleu_result = format_metric(bleu_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references))meteor_result = format_metric(meteor_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references))bertscore_result = bertscore_metric.compute(predictions=predictions, references=references, lang="en")print("Tool Call Accuracy:\n", tool_call_accuracy, "\n")print("Exact Match:\n", exact_match_result, "\n")print("ROUGE:\n", rouge_result, "\n")print("BLEU:\n", bleu_result, "\n")print("METEOR:\n", meteor_result, "\n")print("BERTScore:\n", bertscore_result, "\n")metrics = {"Tool Call Accuracy": tool_call_accuracy,"Exact Match": exact_match_result,"ROUGE": rouge_result,"BLEU": bleu_result,"METEOR": meteor_result,"BERTScore": bertscore_result,}return metrics, tool_call_resultsdef main(repo_id_or_model_path="meta-llama/Llama-3.2-3B-Instruct",disable_adapter=False,lora_adapter_path="outputs/checkpoints/checkpoint-1000",max_seq_length=2048,max_new_tokens=150,temperature=None,top_p=None,top_k=None,min_p=None,num_samples=50,disable_save_results=False,dataset_seed=None,output_dir=None,):dataset_name="Salesforce/xlam-function-calling-60k"# Load model and tokenizermodel, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained(model_name=repo_id_or_model_path,max_seq_length=max_seq_length,device_map="xpu:0",load_in_4bit=False,)if not disable_adapter:if os.path.exists(lora_adapter_path):print("Loading adapter from:", lora_adapter_path)model.load_adapter(lora_adapter_path)else:print(f"Adapter path {lora_adapter_path} does not exist.")raise FileNotFoundError(f"Adapter path {lora_adapter_path} does not exist.")FastLanguageModel.for_inference(model)generation_args = {k: v for k, v in {"max_new_tokens": max_new_tokens,"temperature": temperature,"top_p": top_p,"top_k": top_k,"min_p": min_p,}.items() if v is not None}evaluation_config = {"repo_id_or_model_path": repo_id_or_model_path,"dataset_name": dataset_name,"disable_adapter": disable_adapter,"lora_adapter_path": lora_adapter_path,"max_seq_length": max_seq_length,"num_samples": num_samples,"dataset_seed": dataset_seed,"max_new_tokens": max_new_tokens,"generation_args": generation_args,}# Load datasetdataset = get_dataset(dataset_name, num_samples, dataset_seed)def run_evaluation(**kwargs):return evaluate_model(**kwargs)predictions, references = run_evaluation(model=model,tokenizer=tokenizer,dataset=dataset,generation_args=generation_args)metrics, tool_call_results = compute_metrics(output_dir, predictions, references, disable_save_results, dataset)if not disable_save_results:log_evaluation_results(output_dir, evaluation_config, predictions, references, dataset, metrics, tool_call_results)if __name__ == "__main__":# Set params accordinglymain()
运行效果如下:
4)效果展示:微调后模型已学会“先调用工具,再基于结果回答”
下面是我本地运行 python inference.py 的真实输出,使用如下sample_tools.py中提供的工具(加载 LoRA adapter:checkpoint-1000)。
你会看到一个稳定模式:
模型先输出结构化 tool call JSON → 工具执行返回结果 → 模型再自然语言总结
Case 1:向量求和(结构化参数 + 正确结果归纳)
[Assistant → Tool Call JSON]{"name": "get_vector_sum", "parameters": {"a": [1, -1, 2], "b": [3, 0, -4]}}[Tool → Result][4, -1, -2][Assistant → Final Answer]The sum of vectors a and b is [4, -1, -2].
Case 2:设置提醒(意图抽取为可执行参数)
[Assistant → Tool Call JSON]{"name": "set_reminder", "parameters": {"reminder_text": "Call John", "time": "3 PM tomorrow"}}[Tool → Result]{'status': 'success', 'message': "Reminder set: 'Call John' at 3 PM tomorrow."}[Assistant → Final Answer]Okay, I have set a reminder to call John at 3 PM tomorrow.
Case 3:生成强密码(参数可控 + 工具结果复述)
[Assistant → Tool Call JSON]{"name": "generate_password", "parameters": {"length": 12, "include_numbers": true, "include_symbols": true}}[Tool → Result]{'status': 'success', 'password': ':JlgWf0G8PXa'}[Assistant → Final Answer]The generated password for you is :JlgWf0G8PXa.
Case 4:创建日历事件(时间理解 + schema 稳定)
[Assistant → Tool Call JSON]{"name": "create_calendar_event", "parameters": {"title": "Team Meeting", "start_time": "15th March 10 AM", "end_time": "15th March 12 PM"}}[Tool → Result]{'status': 'success', 'message': "Event 'Team Meeting' created from 15th March 10 AM to 15th March 12 PM."}[Assistant → Final Answer]The event 'Team Meeting' has been successfully added to your calendar from 15th March 10 AM to 15th March 12 PM.
Case 5:带参会人的事件(更复杂 schema + 人类可读重写)
[Assistant → Tool Call JSON]{"name": "create_calendar_event_with_attendees", "parameters": {"title": "Meeting", "start_time": "2024-03-15T10:00:00", "end_time": "2024-03-15T12:00:00", "attendees": ["john@example.com", "jane@example.com"]}}[Tool → Result]{'status': 'success', 'message': "Event 'Meeting' created from 2024-03-15T10:00:00 to 2024-03-15T12:00:00 with attendees: john@example.com, jane@example.com."}[Assistant → Final Answer]Event 'Meeting' has been successfully created for 15th of March 2024, starting from 10 AM and ending at 12 PM. The attendees for this meeting are John and Jane.
5)评测结果:Tool Call Accuracy = 0.78(50 samples)
在 python evaluate.py 的 50 条样本评测中,我得到:
-
Tool Call Accuracy:0.78
-
Exact Match:0.76
-
ROUGE-L:≈0.953
-
BLEU:≈0.96
-
METEOR:≈0.958
这说明:在只训练了 1 epoch / 1000 steps 的情况下,模型已经具备较为可用的工具调用能力。评测日志中也观察到少量长参数样本会出现 JSON 截断导致 parse 失败,这属于 function calling 任务里常见的“长结构输出”挑战,后续可以通过更长训练步数、增加长参数样本比例或结构化约束解码进一步提升。
6)总结:步骤简单,本地 AI PC 也能完成微调闭环
跑通后你会发现:这套流程本质上就是 “装好工具链 → 配好运行时 → 一条命令训练”。
更重要的是:你完全可以在自己的 AI PC 上完成 LoRA 微调、推理验证、评测闭环——无需昂贵独立显卡,也不必上云。这对开发者做个人项目验证、企业内部 PoC、以及端侧 Agent 能力定制,都非常实用。
OpenVINO 小助手微信 : OpenVINO-China
如需咨询或交流相关信息,欢迎添加OpenVINO小助手微信,加入专属社群,与技术专家实时沟通互动。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献303条内容
已为社区贡献303条内容








所有评论(0)