Guide: Multi-Arc Solution of LLM Inference based Arc Pro B60
Xeon platform with 2x, 4x or 8x Arc Pro B60, and setup power for each GPU.
1.1 Xeon Platform with multi-arc Pro B60
Xeon platform with 2x, 4x or 8x Arc Pro B60, and setup power for each GPU.
1.2 Set BIOS option
Enable Re-Size BAR Support and PCIe Gen5 X8X8 as below:
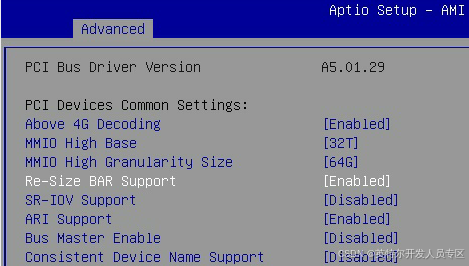
Socket Configuration->IIO Configuration->Socket1 Configuration
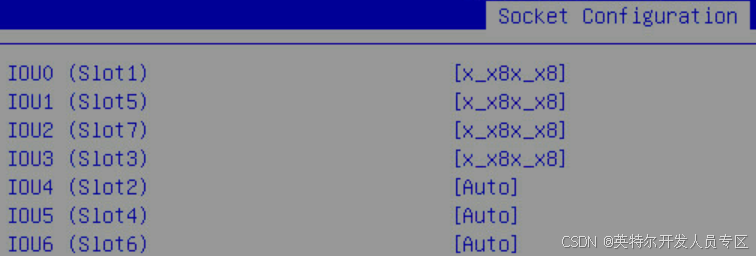
If you have a dual-core GPU, this setting is mandatory.
Socket Configuration->IIO Configuration->Intel VT for Directed I/O(VT-d)
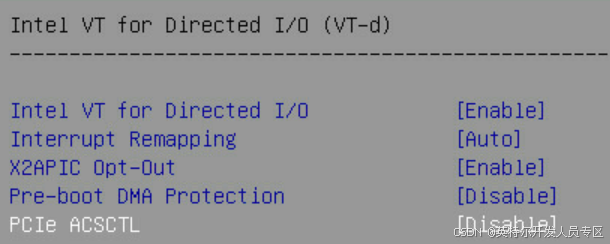
Mark: This option is related to P2P communication, must be disabled.
2. SW Installation & Configuration
Software configuration is as follows:
|
SW Configuration |
|
|
OS |
Ubuntu 25.04 |
|
Kernel |
6.14.0-1011-intel |
|
Driver |
multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1 |
|
vLLM Serving |
intel/llm-scaler-vllm:1.3 |
2.1 OS Installation
Install Ubuntu 25.04 according to the URL:
Ubuntu25.04-desktop:
https://releases.ubuntu.com/25.04/ubuntu-25.04-desktop-amd64.iso
Mark: if you install desktop OS, you must unplug GPU power cable. After the installation of driver is complete, then connect the power cord.
Ubuntu25.04-server(Normal install)
https://mirrors.xjtu.edu.cn/ubuntu-releases/25.04/ubuntu-25.04-live-server-amd64.iso
2.2 HW Verification
Keep power is enough for multi-GPUs and install Arc Pro B60 in platform, then check PCIe status:
~$ lspci | grep e211
18:00.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Device e211
36:00.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Device e211
54:00.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Device e211
cc:00.0 VGA compatible controller: Intel Corporation Device e211
2.3 Driver Offline Installation
Download offline driver from this URL:
Let’s use Ubuntu 25.04-Desktop as an example for the installation.
Make sure APT network is connected and your account has sudo permissions, install driver as below:
~$ wget https://cdrdv2.intel.com/v1/dl/getContent/873591/873592?filename=multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1.tar.xz -O multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1.tar.xzInstall offline driver as below:
~$ xz -d multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1.tar.xz
~$ tar -xvf multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1.tar
~$ cd multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1If you perform an upgrade installation (Option)
~$ sudo apt --fix-broken install
~$ sudo apt autoremoveInstall driver by default.
~$ sudo ./installer.shWait a few seconds, you can see the success log as below:
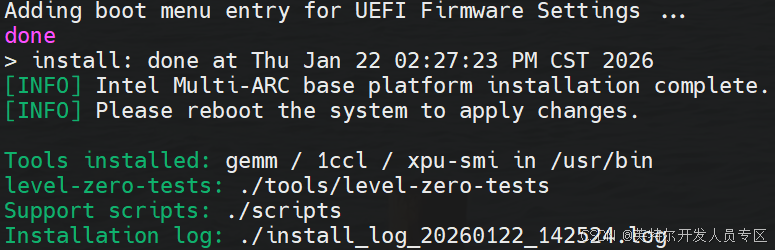
~$ sudo reboot
~$ uname -r6.14.0-1011-intel
Fixed Kernel as below:
~$ sudo apt-mark hold linux-image-generic linux-headers-genericDisable software update by modifying configuration APT::Periodic::Update-Package-Lists from "1" to "0":
~$ sudo vim /etc/apt/apt.conf.d/10periodic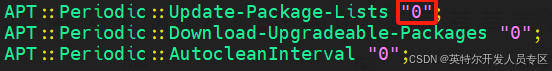
Add current user into render group as below:
~$ sudo gpasswd -a ${USER} render
~$ sudo newgrp render
~$ sudo rebootVerify GPU status:
~$ xpu-smi discovery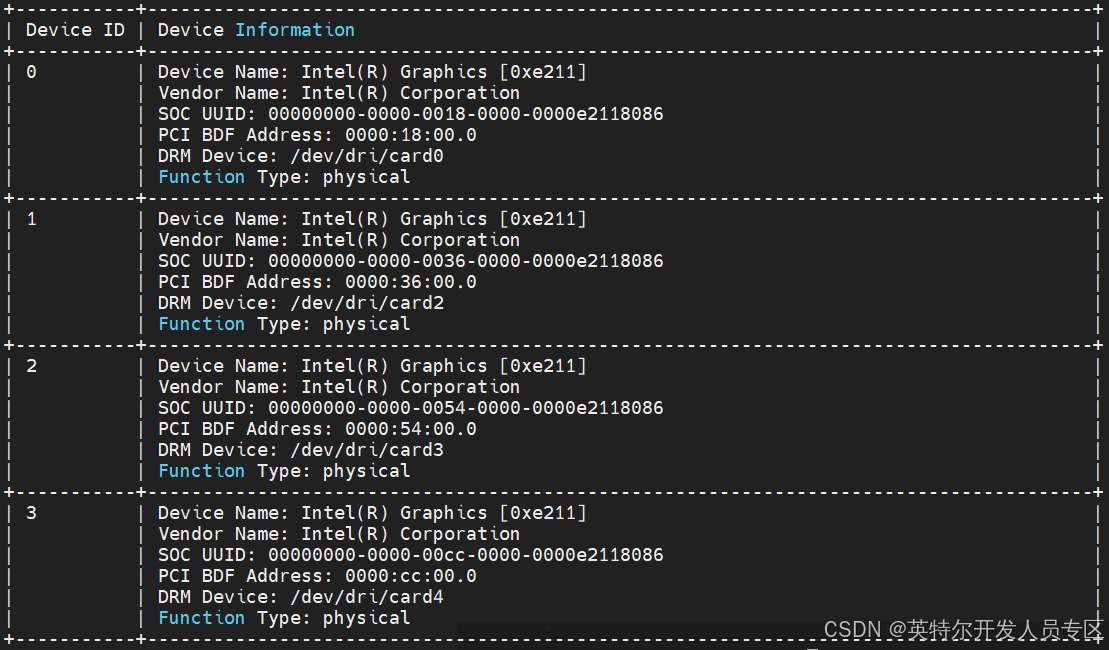
View driver version as below:
~$ source /opt/intel/oneapi/setvars.sh
~$ sycl-ls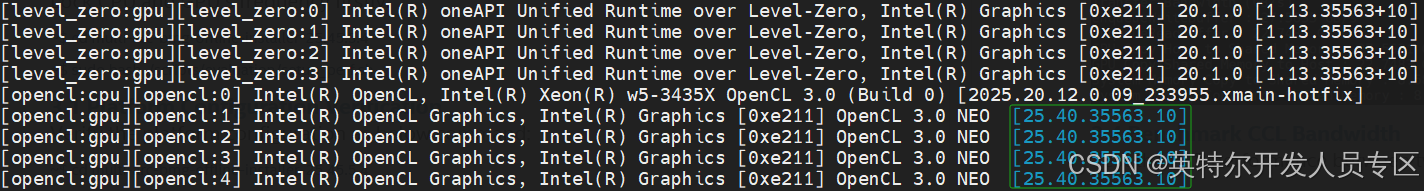
2.4 System Mode Setting (Optional)
If you install desktop system, you must set system to graphical mode.
~$ sudo systemctl get-defaultIf return multi-user.target, you can change it to graphical mode.
~$ sudo systemctl set-default graphical.target3. Platform Verification & Benchmark
Benchmark memory bandwidth, host to GPU bandwidth, allreduce etc.
Lock CPU and GPU’s frequency firstly:
~$ cd multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1
~$ sudo bash ./scripts/evaluation/setup_perf.sh3.1 Platform Configuration Verification
Verify the platform configuration as below command:
~$ cd multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1
~$ sudo bash scripts/evaluation/platform_basic_evaluation.sh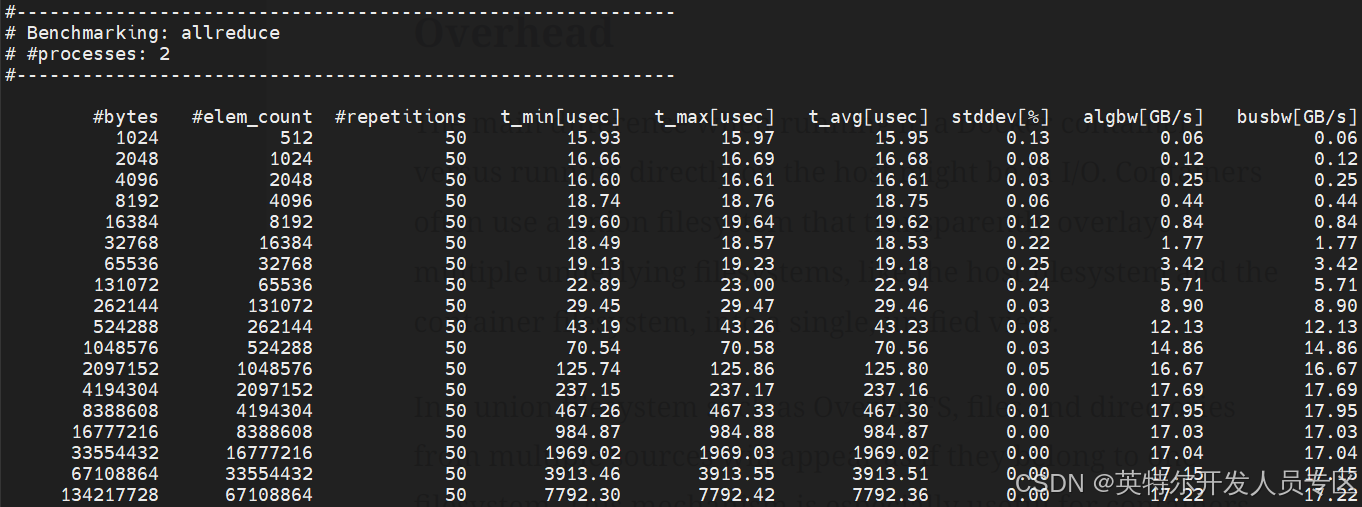
Wait several minutes, log file will be generated such as results/*/benchmark_detail_log.txt
3.2 Memory Bandwidth test
Test GPU’s bandwidth as below:
~$ export NEOReadDebugKeys=1
~$ export RenderCompressedBuffersEnabled=0
~$ xpu-smi diag --singletest 3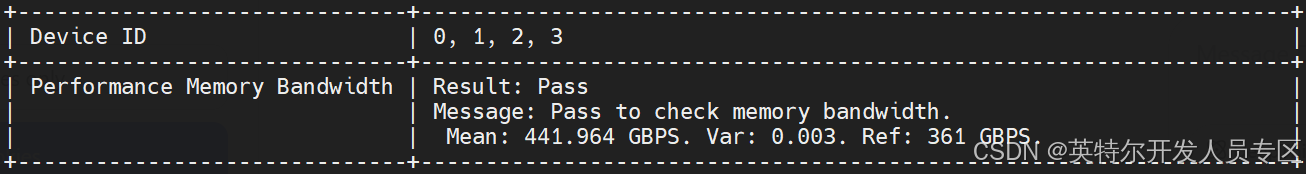
3.3 benchmark bandwidth between Host and GPU
Test GPU 0 bandwidth between host and GPU:
~$ cd multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1/tools/level-zero-tests
~$ sudo ./ze_peak -t transfer_bw -d 0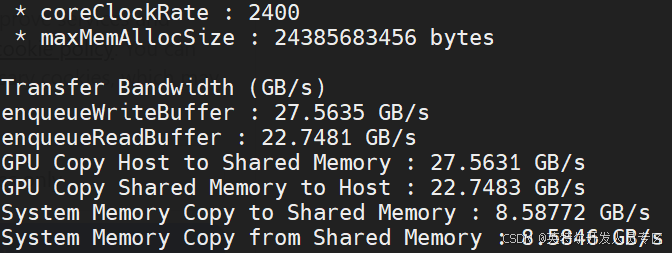
3.4 Benchmark CCL Bandwidth
Test the P2P performance between two CPUs.
~$ cd multi-arc-bmg-offline-installer-26.5.6.1/tools/level-zero-testsTest Unidirectional communication P2P performance:
~$ sudo ./ze_peer -t transfer_bw -o write --parallel_pair_targets 0:1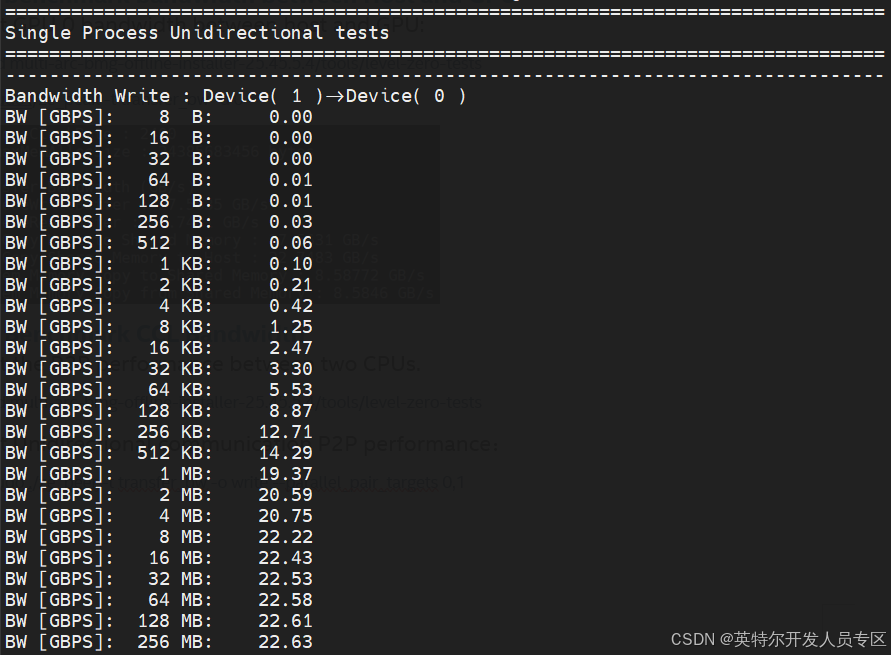
Test bidirectional communication P2P performance:
~$ sudo ./ze_peer -t transfer_bw -o write --parallel_pair_targets 0:1 -b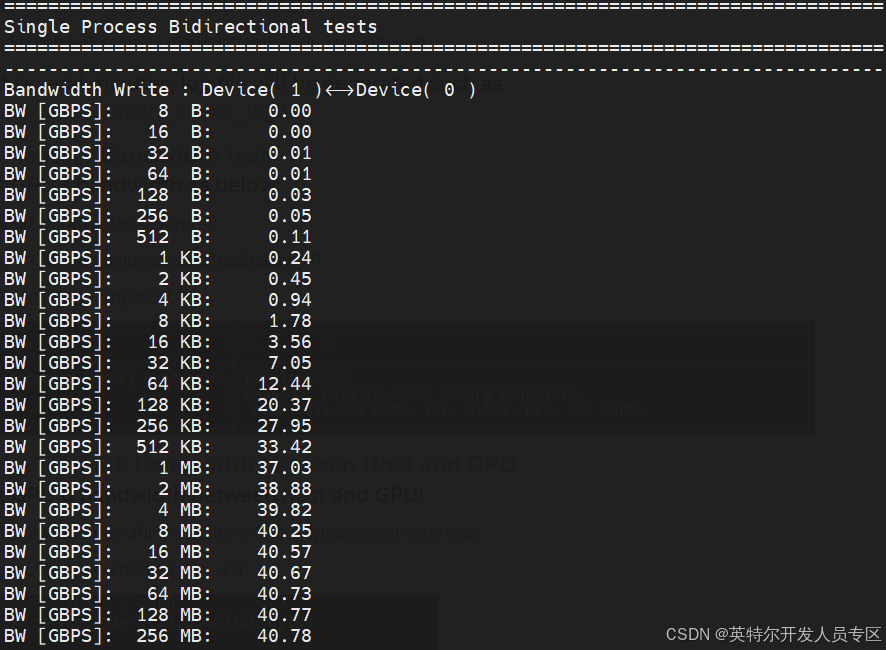
4. GPU Visualization
4.1 GPU Isolation for Container
This is a common requirement for virtualization orchestration, we need isolate some GPUs for containers, GPU isolation can be achieved in the following ways:
1. Remove --privileged and --device=/dev/dri
2. Add the following options
--device /dev/dri/renderD128:/dev/dri/renderD128 \
--mount type=bind,source="/dev/dri/by-path/pci-0000:18:00.0-card",target="/dev/dri/by-path/pci-0000:18:00.0-card" \
--mount type=bind,source="/dev/dri/by-path/pci-0000:18:00.0-render",target="/dev/dri/by-path/pci-0000:18:00.0-render" \
-v /dev/dri/card0:/dev/dri/card0 \Based above method, GPU0 can be bound to a container, Ensure the PCIe ID of this device is aligned correctly (Marked in orange).
5. LLM Serving & Benchmark
Install docker refers to link Install Docker Engine on Ubuntu | Docker Docs
For detailed installation instructions, please refer to Section 6.1
5.1 Download Docker Image & LLM Models
Download intel vllm version as below:
~$ docker pull intel/llm-scaler-vllm:1.2Download LLM model from https://hf-mirror.com in your folder (for example: /home/${USER}/LLM):
Download distilled model from https://hf-mirror.com/collections/Qwen/qwen3
5.2 Text Generation LLM Serving
Put below script into docker-backend.sh in /home/user/llm-server:
#!/bin/bash
export DOCKER_IMAGE=intel/llm-scaler-vllm:1.3
export CONTAINER_NAME=llm-serving
docker rm -f $CONTAINER_NAME
sudo docker run -td \
--privileged \
--net=host \
--device=/dev/dri \
--name=$CONTAINER_NAME \
-v /home/user/LLM:/llm/models/ \
-v /home/user/llm-server:/llm/ \
-e no_proxy=localhost,127.0.0.1 \
--shm-size="32g" \
--entrypoint /bin/bash \
$DOCKER_IMAGEPut below script into vllm-qwen3-32b-openaikey.sh:
#!/bin/bash
model="/llm/models/Qwen3-32B"
served_model_name="Qwen3-32B"
export TORCH_LLM_ALLREDUCE=1
export VLLM_USE_V1=1
export CCL_ZE_IPC_EXCHANGE=pidfd
export VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1
export VLLM_WORKER_MULTIPROC_METHOD=spawn
python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model $model \
--served-model-name $served_model_name \
--dtype=float16 \
--enforce-eager \
--port 8001 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--api-key intel123 \
--trust-remote-code \
--disable-sliding-window \
--gpu-memory-util=0.9 \
--max-num-batched-tokens=10000 \
--disable-log-requests \
--max-model-len=10000 \
--block-size 64 \
--quantization fp8 \
-tp=4Then start the container and vllm serving:
~$ sudo bash docker-backend.sh
~$ docker exec -it llm-serving bash
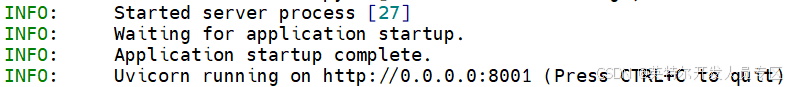
~$ bash vllm-qwen3-32b-openaikey.shWhen you see log as below, the service is successful:
Verify LLM serving by command as below script test.sh:
#!/bin/bash
if [ $# -eq 3 ]; then
MODEL=$1
API_KEY=$2
PROMPT=$3
else
echo "Please add input parameters"
echo "bash bash.sh Qwen3-32B api_key input_prompt"
exit
fi
echo "Prompt: "$PROMPT
# 流式对话函数
stream_chat() {
local model="$1"
local api_key="$2"
local prompt="$3"
curl -s -X POST http://localhost:8001/v1/chat/completions -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer '"$api_key"'" \
-N \
-d '{
"model": "'"$model"'",
"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "'"$prompt"'"}],
"temperature": 0.7,
"max_tokens": 512,
"stream": true}' | while IFS= read -r line; do
if [[ $line == data:* ]]; then
local json="${line:6}"
[ "$json" == "[DONE]" ] && break
local content=$(echo "$json" | jq -r '.choices[0].delta.content // empty')
if [ -n "$content" ]; then
printf "%s" "$content"
sleep 0.02
fi
fi
done
echo
}
stream_chat $MODEL $API_KEY $PROMPTexecute this shell script as below:
~$ bash test.sh Qwen3-32B intel123 "写一段关于人工智能的科普短文"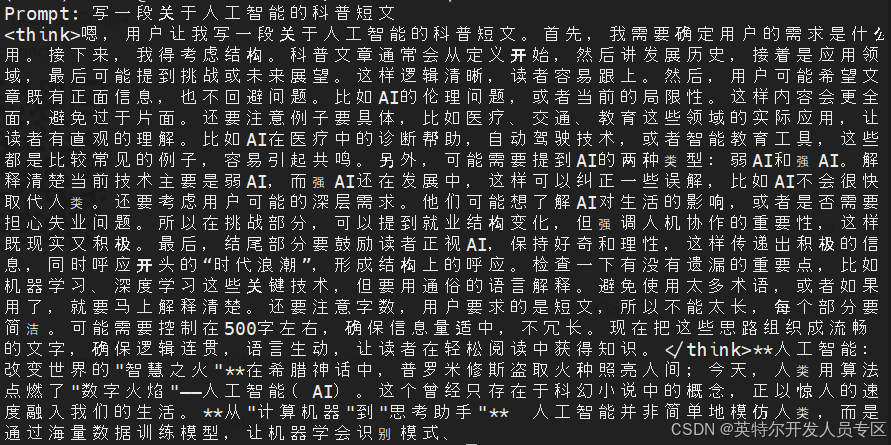
5.3 Multimodal LLM Serving
Download Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct from Huggingface.
Put below script into vllm-qwen2.5-vl-32b-instruct-openaikey.sh:
#!/bin/bash
model="/llm/models/Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Inastruct"
served_model_name="Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Inastruct"
export TORCH_LLM_ALLREDUCE=1
export VLLM_USE_V1=1
export CCL_ZE_IPC_EXCHANGE=pidfd
export VLLM_ALLOW_LONG_MAX_MODEL_LEN=1
export VLLM_WORKER_MULTIPROC_METHOD=spawn
python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server \
--model $model \
--served-model-name $served_model_name \
--allowed-local-media-path /llm/models/test \
--dtype=float16 \
--enforce-eager \
--port 8001 \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--api-key intel123 \
--trust-remote-code \
--gpu-memory-util=0.9 \
--max-num-batched-tokens=8192 \
--disable-log-requests \
--max-model-len=8192 \
--block-size 64 \
--quantization fp8 \
-tp=4Then start the container and vllm serving:
~$ sudo bash docker-backend.sh
~$ docker exec -it llm-serving bash
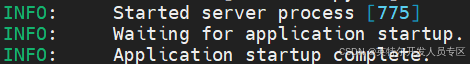
~$ bash vllm-qwen2.5-vl-32b-instruct-openaikey.shWhen you see log as below, the service is successful:
Verify LLM serving by command as below:
~$ curl http://localhost:8001/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer intel123" \
-d '{
"model": "Qwen2.5-VL-32B-Instruct",
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "图片里有什么?"
},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "http://farm6.staticflickr.com/5268/5602445367_3504763978_z.jpg"
}
}
]
}
],
"max_tokens": 128
}'Output is as below:
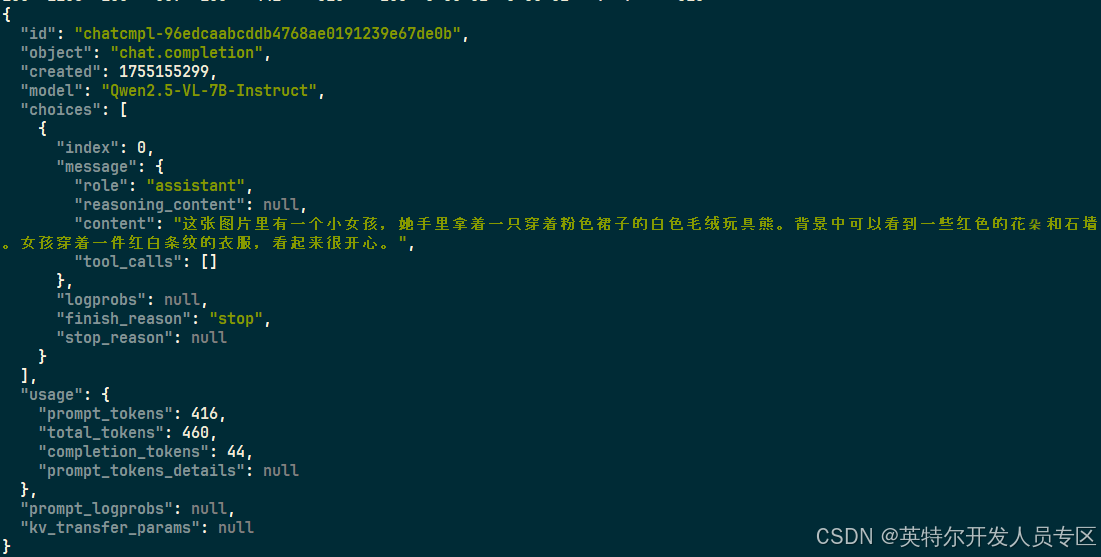
6. Appendix
6.1 Docker Installation
Install docker refers to link Install Docker Engine on Ubuntu | Docker Docs
~$ sudo apt update
~$ sudo apt install ca-certificates curl
~$ sudo install -m 0755 -d /etc/apt/keyrings
~$ sudo curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
~$ sudo chmod a+r /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc# Add the repository to Apt sources:
~$ sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.sources <<EOF
Types: deb
URIs: https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu
Suites: $(. /etc/os-release && echo "${UBUNTU_CODENAME:-$VERSION_CODENAME}")
Components: stable
Signed-By: /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.asc
EOF
~$ sudo apt update
~$ sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-pluginAdd user account into docker group:
~$ sudo gpasswd -a ${USER} docker
~$ sudo newgrp docker6.2 KVM Installation
The working principle of KVM is as follows:
Physical GPU → VFIO Driver (Host)→ Passthrough → Virtual Machine → GPU Driver
Mark: Host platform does not require driver installation beforehand.
BIOS configuration is as below:
- Set BIOS Configuration to enable virtualization in BIOS:
Socket Configuration -> Processor Configuration-> VMX = Enabled
- Configure kernel command-line parameters by adding “iommu=pt intel_iommu=on” to line GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT as below:
~$ sudo vim /etc/default/grub

If you use graphical mode, please modify graphics.cfg as below:
~$ sudo vim /etc/default/grub.d/graphics.cfgGRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT="$GRUB_CMDLINE_LINUX_DEFAULT iommu=pt intel_iommu=on"
Then reboot the OS to take effect.
~$ sudo update-grub
~$ sudo reboot
~$ sudo dmesg | grep -i iommuInstall KVM package as below:
~$ sudo apt update
~$ sudo apt install -y qemu-kvm libvirt-daemon-system libvirt-clients bridge-utils virt-manager ovmf
~$ sudo apt install -y cpu-checker # Add user into group
~$ sudo adduser $USER libvirt
~$ sudo adduser $USER kvm
~$ kvm-okINFO: /dev/kvm exists
KVM acceleration can be used
Then leverage virt-install and virsh to install and manage virtual machines.
OpenVINO 小助手微信 : OpenVINO-China
如需咨询或交流相关信息,欢迎添加OpenVINO小助手微信,加入专属社群,与技术专家实时沟通互动。
更多推荐
 已为社区贡献303条内容
已为社区贡献303条内容









所有评论(0)